Microfluidizer® Technology for
Nanoparticle Albumin Bound (nab) Drug Delivery
Nanoparticle albumin-bound (nab) drug delivery is a promising platform due to albumin’s biocompatibility and effectiveness as a drug carrier. In this application note, we explore how Microfluidizer® Technology can be used to create stable nanoemulsions for the formulation of nab nanoparticles.
 Scalable
Scalable
Results
 cGMP
cGMP
Focus
 Stable
Stable
Nanoemulsions

BACKGROUND
How is nab technology used in cancer treatments?
Cancer treatments have made significant progress in recent years, with chemotherapy remaining a widely used approach. However, delivering these medications is challenging due to their high toxicity, poor water solubility, and limited bioavailability. Conventional delivery agents like Cremophor EL and ethanol can also cause serious side effects, including severe allergic reactions.
Nanoparticle albumin-bound (nab) technology offers a promising alternative. Albumin, as a naturally abundant plasma protein, provides a safe, biocompatible, and biodegradable delivery platform. The first FDA-approved chemotherapy drug using this technology was Abraxane® (Nab-paclitaxel), which has achieved notable success. This Application Note explores how forming stable nanoemulsions supports the effectiveness of this drug.
THE CHALLENGE
Achieving precise, sterile nanoemulsions
Abraxane® is prescribed for advanced pancreatic cancer, metastatic breast cancer, and non-small cell lung cancer. Albumin, a natural protein in the blood, is ideally suited for transporting therapeutic agents directly to tumor sites. In Abraxane®, human serum albumin (HSA) delivers the chemotherapy drug paclitaxel to cancer cells through multiple pathways, preventing their division and leading to cell death.
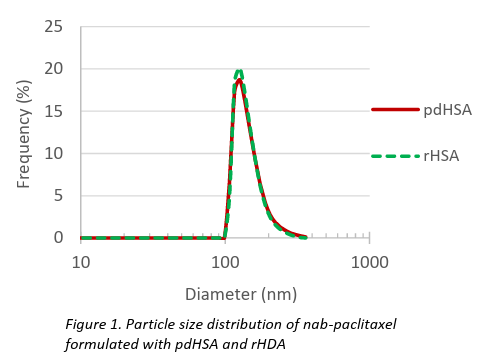
However, simply mixing paclitaxel and albumin is not effective—they must be combined and processed into a suitable form. Like many cancer therapies, Abraxane® is given to patients by intravenous infusion, so it must be sterile. Filter sterilization is preferred, requiring a precise average particle size of 130 nanometers and a consistent distribution. Achieving this particle size is also essential for later stages, such as solvent removal and freeze-drying. Selecting the right processing technology is critical to producing stable nab particles.
APPLICATION
Microfluidizer® Technology for nab formulations
A leading approach for creating nab-paclitaxel nanoparticles is emulsification. In this process, paclitaxel is dissolved in a water-immiscible organic solvent to form an oil phase. This is mixed with an an aqueous albumin solution to form a coarse emulsion, which is then refined using high-shear Microfluidizer® technology to achieve uniform droplet size and distribution. The emulsion then undergoes solvent removal, sterilization, and freeze-drying (lyophilization) to yield a powder product.
In this study, both plasma-derived HSA (pdHSA, provided by Biotest AG) and recombinant HSA (rHSA) were used to prepare nab-paclitaxel with a benchtop LM20 Microfluidizer® processor.
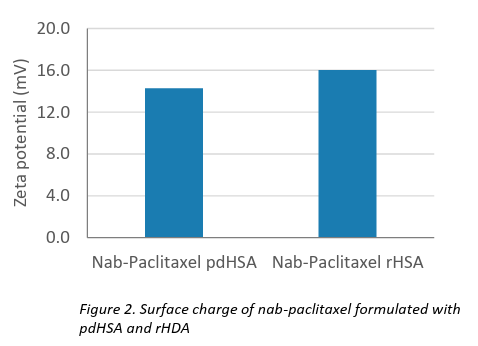
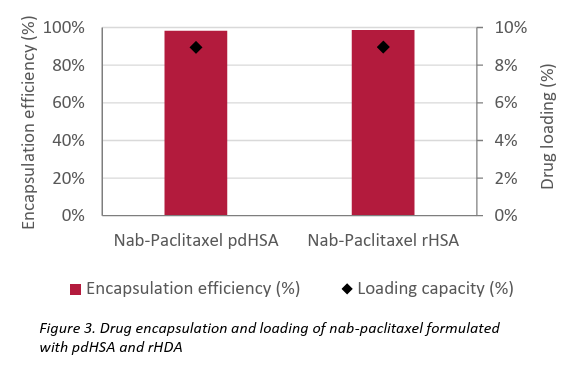
The resulting nanoparticles were evaluated for particle size, size distribution, zeta potential, and encapsulation efficiency. Both formulations produced particles sized approximately 130–140 nm with a narrow polydispersity index (PdI), and demonstrated moderate colloidal stability, as highlighted in Table 1 and Figures 1 & 2. These results are comparable to those of the commercial product Abraxane®. High encapsulation efficiency (~98%) and drug loading (~9%) were achieved in both cases.
| Formulation | Z-Average Size | PDI |
| nab-Paclitaxel (pdHSA) | 129.18 | 0.208 |
| nab-Paclitaxel (rHSA) | 134.97 | 0.215 |
BENEFITS
Benefits of Microfluidizer® Technology for nab Paclitaxel Drug Delivery
Microfluidizer® technology is ideal for creating nab nanoparticles. With a proven track record of creating best-in-class nanoemulsions, this technology can:
- Create desired droplet sizes with narrow particle size distribution
- Achieve consistent results to ensure batch-to-batch repeatability
- Enable easier down-stream, e.g., sterile filtration, processes
Microfluidizer® processors deliver results that are fully scalable from laboratory to production. Because every model uses the same fixed-geometry Interaction Chamber™, process outcomes achieved during R&D are reliably reproduced at manufacturing scale. This ensures consistent product quality at any volume, providing complete confidence as you move from pilot to full production.
Microfluidizer® processors also significantly outperform conventional high-pressure homogenizers (HPH) in producing effective nanoemulsions. Our data repeatedly shows that the Microfluidizer® processor is much more efficient in producing more uniform nanoemulsions when compared to HPH. Whilst also consuming much less energy than HPH. Microfluidizer® processors are also:
- Easy to operate
- Reliable with low maintenance cost
- Linearly scalable from 2ml to Liters per hour
- Compliant with cGMP regulation
Get your free copy.
Open this application note in a downloadable format.
FURTHER RESOURCES
You may also be interested in these articles:
Brochure: Processors for Nanotechnology Application Challenges
Learn how Microfluidizer® technology produces unrivaled results in uniform nanoemulsions, cell disruption and particle size reduction.
 Explore
Explore
Webinar: nab Paclitaxel using Microfluidizer® Technology
Comparison of Biotest HSA and Recombinant HSA for the Preparation of Nano Albumin Bound (nab) Paclitaxel using Microfluidizer® Technology.
 Explore
Explore
How it Works: Microfluidizer® Technology
Microfluidizer® Technology delivers superior results by combining a constant pressure pumping system with a unique fixed-geometry Interaction Chamber™.
 Explore
Explore